Ethereum: Does a blockchain without a currency make sense?
In recent years, interest in blockchain technology has grown, especially among private companies looking to harness its potential for a variety of commercial applications. One of the most interesting aspects of blockchain is its ability to enable decentralized transactions and data storage without the use of traditional currencies. But does this concept make sense when applied to everyday life?
To understand the allure of a blockchain-free economy, let’s take a look at what we know about Ethereum and the technology behind it.
What is Ethereum?
Ethereum (ETH) is an open-source blockchain platform that allows developers to create and deploy smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps). Founded in 2014 by Vitalik Buterin, it has since gained popularity due to its scalability, security, and usability. Ethereum’s native cryptocurrency, Ether (ETH), is used not only as a store of value, but also as a fuel for transaction fees on the network.
Smart Contracts: The Backbone of the Blockchain
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts whose contractual terms are written directly into lines of code. They can automate processes such as payments and property transfers without the need for intermediaries such as banks or governments. On Ethereum, smart contracts run entirely on the blockchain, allowing users to enforce their own contracts without the need for a central authority.
Why do businesses want a coinless blockchain?
Private businesses are attracted to blockchain technology for several reasons:
- Increased efficiency: Blockchain-based systems can process transactions faster and cheaper than traditional methods.
- Enhanced security: Smart contracts on Ethereum ensure that all parties involved in a transaction are trustworthy and adhere to the agreed-upon rules.
- Reduced number of intermediaries: By eliminating the need for intermediaries, businesses can save on costs associated with payment processing fees and transaction verification.
Ethereum Blockchain: A Decentralized Database
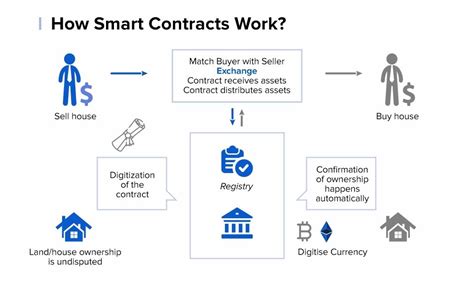
The Ethereum network is a decentralized database that stores its data on a blockchain. This means that all transactions, smart contracts, and decentralized applications are stored on a single chain, making it difficult to manipulate or alter the data.
While this decentralized architecture has many advantages, it also has some potential drawbacks:
- Scalability: Ethereum’s current scalability is limited, which can lead to congestion and slow transaction processing times.
- Energy consumption: The Ethereum network requires significant energy consumption to maintain the blockchain, which can be an environmental concern.
Does Blockchain Make Sense Without Currency?
Ultimately, while blockchain technology has many interesting applications, it may not make sense to build a decentralized economy without traditional currencies. Here are some reasons why.
- Economic Incentives: Currencies provide economic incentives for individuals and businesses to participate in the market, such as promising higher returns on investment.
- Social Benefits: Traditional currencies also facilitate social interaction, trade, and commerce, which are essential aspects of human society.
- Regulatory Frameworks: Governments and regulators have created frameworks for the use of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin that provide a level of protection and stability for participants.
However, Ethereum smart contracts can still enable decentralized applications that create value without relying on traditional currencies. For example:
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Ethereum smart contracts can facilitate decentralized lending, borrowing, and other financial services.
2.


